Ebola virus epidemic is one of the most discussed topics in recent months, causing panic worldwide since the epidemic came outside Africa. What you need to know about one of the most dangerous and deadly viruses known to man?
RNA virus
Ebola is an RNA virus that infects wild animals (fruit bats, monkeys, gorillas, chimpanzees) and humans. It is believed that the source of the outbreak is contact with blood of an infected animal.
Its name
The name of the Ebola virus comes from the geographical region where first discovered it. It is named after the Ebola River, located in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
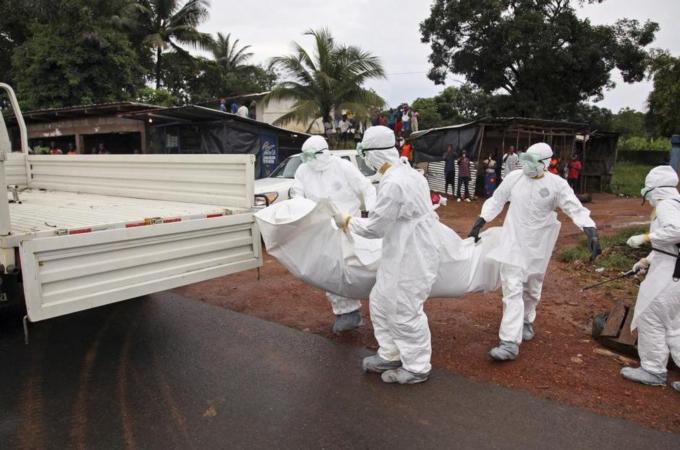

Еpidemic
The first outbreak of Ebola was registered in 1975 in the Democratic Republic of Congo (then Zaire). There are virus infected 318 people, 280 of them have died. In the same year the virus infected 284 people in Sudan, killing 151.
The current epidemic is far greater. In Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia, 15 October 2014 registered 8,973 cases of people infected with Ebola. Another 24 cases were registered even in Nigeria, Senegal, Spain and the US, and 68 in the Democratic Republic of Congo. People at greatest risk are those who have been in close contact with infected individuals.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
The first symptoms of Ebola are fever, headache, cough, stomach pain, vomiting and diarrhea. For what are the symptoms of many other diseases, from the common cold to the flu, early diagnosis of Ebola is extremely difficult.
Incubation of the infected with Ebola is between 2 and 21 days. Most infected showing first symptoms of disease 8-9 days after exposure to the virus.
A few days after the first symptoms of Ebola appear more serious ones. Due to internal and external bleeding, the patient’s eyes turn red, one begins to vomit blood, cardiovascular collapse, leading to death.
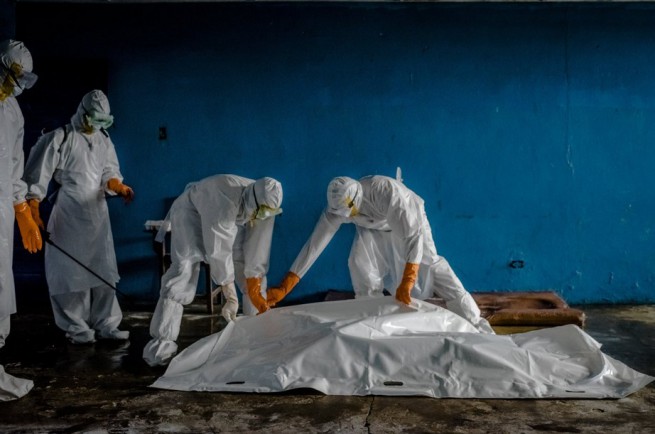

Extremely high mortality
Ebola has a very high mortality rate – from 50% to 90%. About half of those infected in West Africa have died. This means that the chances of survival are quite small, and late detection of the disease is almost always fatal.
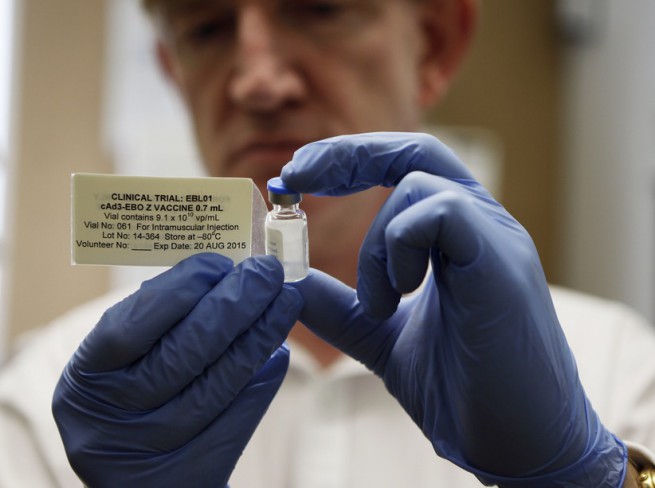
There is no vaccine against Ebola
Currently developed vaccines against Ebola tested on animals and have had more or less effective. Tests on monkeys, however, were greeted with a lot of resistance, because the populations of monkeys decreased and many species are on the brink of extinction. Testing of the vaccine in humans is much more difficult, but we make efforts in this direction.
New drugs
There is still no approved drug for Ebola and haven’t made such tests on humans. Two American doctors who have been infected with Ebola in Liberia, however, have received experimental treatment with a drug that is still in the early stages of research.
Contamination
The spread of the Ebola virus from one person to another can be done in several ways, but always through direct contact. Patient excreted virus from all your bodily secretions and skin, infection can happen to touch.
You can not get infected with Ebola in the air or water nor food. Epidemic in Africa, however, may be broken as a result of the processing of game meat and contact with infected bats. There is no evidence mosquitoes or other insects carry the virus. Only mammals can become infected and spread ebola. Another reason for the growth of the epidemic in Africa are poor living conditions and well-equipped medical personnel who treated the sick.
If you survive and recover from Ebola, it ceases to be contaminants and develop immunity, but the virus remains in the male reproductive system to 3 months thereafter, which means that cured men can compromise their sexual partners.